Infectious diseases are major diseases that seriously threaten human health in today's world. Rapid and accurate diagnosis is an important prerequisite for effective treatment, disease monitoring, and control of the spread of diseases. With the continuous development and improvement of molecular detection technology, the clinical application of molecular detection in pathogenic microbial infection diagnosis and treatment monitoring has become increasingly widespread, and it has become an indispensable tool in the diagnosis and efficacy eva1uation of some important infectious diseases.
With the deepening of basic research and technological progress, the recognition process of pathogenic microorganisms and the detection market are also growing. In order to meet future development needs, AMTK has launched a series of automated workstation integration solutions, mainly distributed in qPCR detection and NGS detection In these two application areas, the entire process is convenient and fast, the results are accurate, the pollution rate is low, and the degree of automation is high. It serves well in blood stations, hospitals, disease control centers, third-party medical laboratories and other institutions.
After collecting and extracting suspected infected specimens, directly perform high-throughput sequencing. Through the comparison of pathogenic microorganisms special database and intelligent algorithm analysis, the species information of suspected pathogenic microorganisms is obtained, and comprehensive and in-depth reports are provided to provide fast speed for difficult and critical infections. Accurate diagnosis basis to promote the rational use of antibiotics.
Pathogenic microorganism NGS detection flow chart
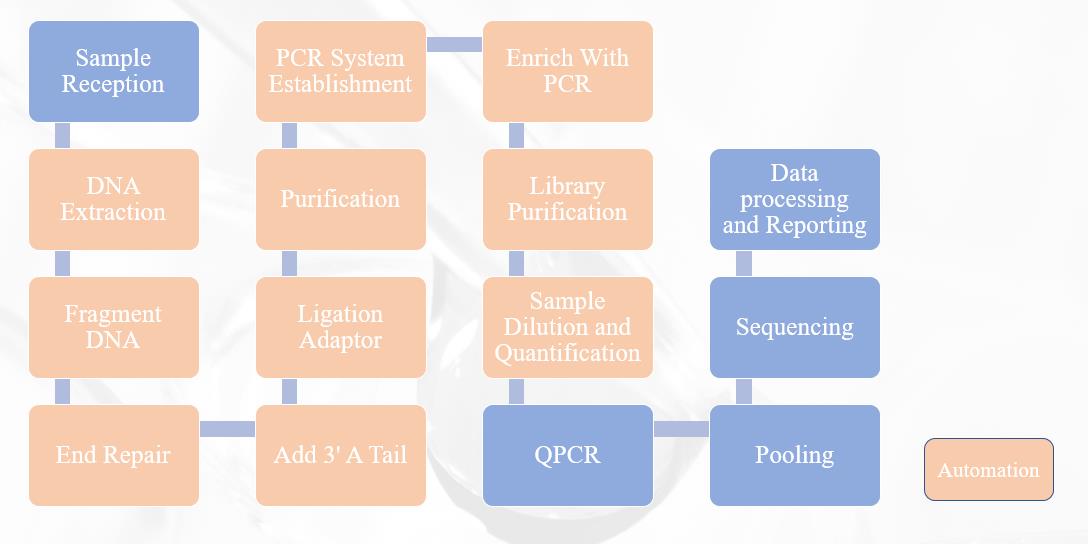
Workstation configuration

LH-1406
Experimental data case
Comparison of qPCR data between manual and automated workstations after 16 Libraries are constructed
qPCR concentration
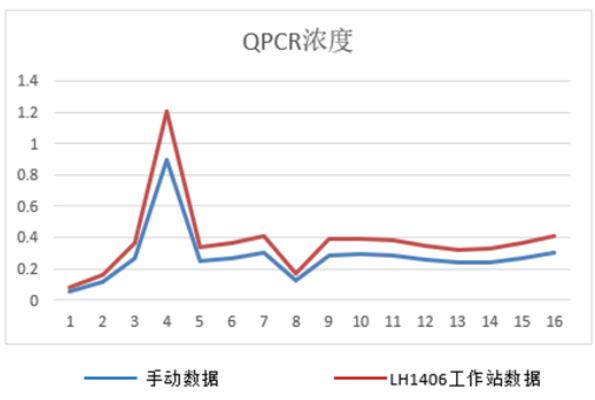
Manual data Workstation data
The data shows that there is no significant difference between automated and manual quantitative qPCR results, and the data accuracy rate is higher.